KIMaps
| Funding Agency: | BMBF |
| Duration: | 3 years, 01.07.2020 - 30.06.2023 |
| Partners: | NavVis GmbH, Hemminger Ingenieurbüro GmbH & Co. KG |
| Contact Persons: | Martin Piccolrovazzi |
| Michael Adam |
Scope of the project
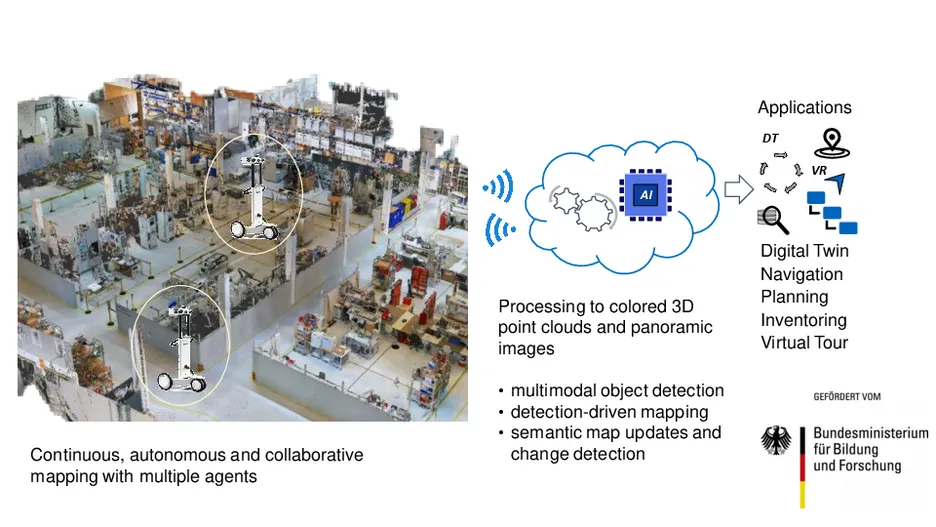
A digital twin (DT) is a digital replica of real world object, process or environment which is used for simulation, optimization and planning. Geometrical digital twins consist of panoramic views and colored 3D point clouds and can be recorded using modern mapping hardware. However, industrial and production environments have become quite dynamic and reconfigurable, while up-to-date maps are required for numerous applications. Even state-of-the-art mapping systems such as the NavVis M6 and VLX are not designed to continuously scan such environments for the creation of up-to-date maps.
The goal of the project KIMaps is to research and develop new methods for the autonomous and continuous creation of digital twins. For the continuous mapping aspect, autonomous agents are used, which consist of an automated guided vehicle (AGV) and a mapping system from the NavVis GmbH. Furthermore, multiple agents are used in a collaborative mapping framework in order to continuously scan large-scale environments. The aim is to provide up-to-date semantic digital models of an environment by developing an AI-based object recognition system to automatically recognize individual objects in 3D point clouds and panoramic views. Further system components that are necessary for the continuous creation of digital twins, in particular the path optimization with regard to object recognition, the change detection and the map update components build upon the object recognition system.
The acquired data and the semantic description of the objects in industrial environments can be embedded in other complex products, services and business models. Changes can thus be displayed on a semantic level and compared with existing 3D models. Up-to-date digital maps enable applications such as object search, inventorying, localization, indoor navigation and virtual training courses. They also make it easier to collaborate with suppliers by sharing the maps, which also reduces travel costs. The developed methods are validated at different locations of associated partners from various industry sectors.
This work is funded by Germany’s Federal Ministry of Education and Research on the basis of a resolution of the German Bundestag under project KIMaps (grant ID #01IS20031C).